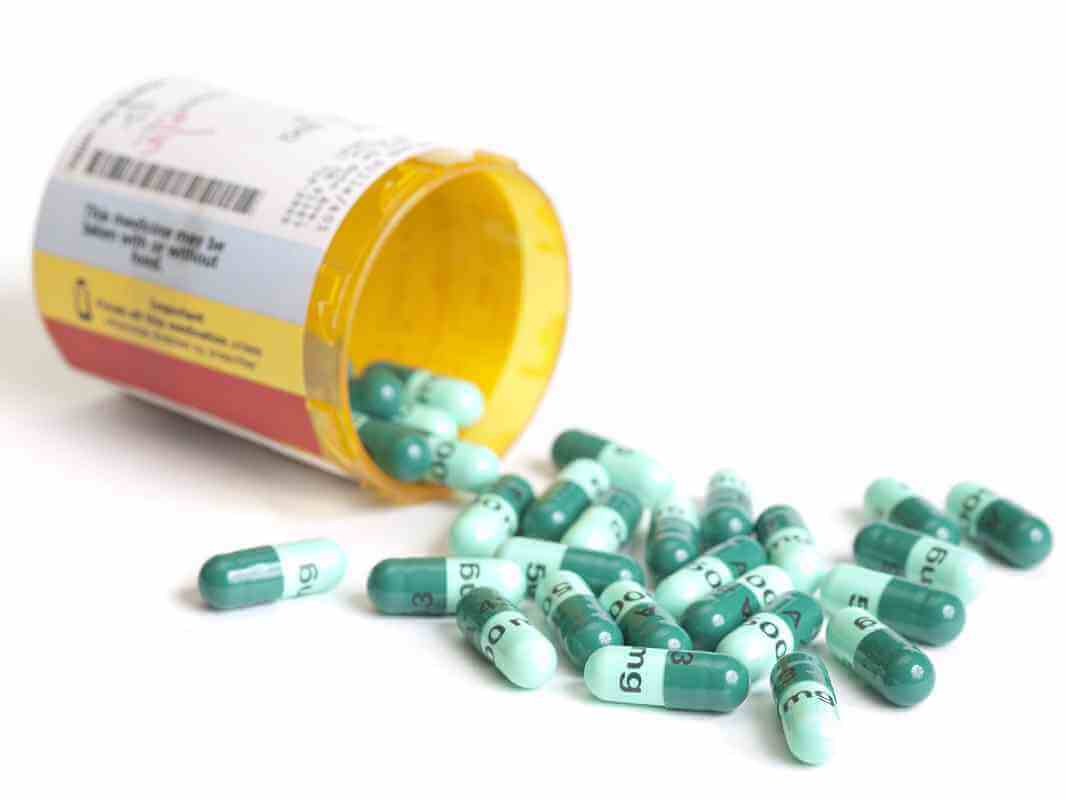
Antibiotics have played an important role in treating and preventing infectious disease for the last century. But how has it affected our health, longevity and resistance to disease?
In our modern medical history in 19th century France, two theories competed. Louis Pasteur, known as the father of germ theory, stated that microorganisms were the root cause of disease. His theory of germophobia has dominated Western medicine giving rise to vaccines, antibiotics and antimicrobials. A competing theory by Antoine Béchamp proposed that the germs both opportunistically cause disease when the conditions are right, but also support our health in a relationship of symbiosis. He believed in not killing the germs but cultivating strong immune system and robust health through diet, hygiene and a healthy lifestyle. Pasteur’s theory became the dominant theory of medicine as Béchamp was all but forgotten.
The introduction of penicillin in the 1940’s is considered the beginning of the antibiotic era. Thought to be one of the greatest advances in therapeutic medicine, it treated life threatening infectious diseases such as syphilis, gangrene and tuberculosis. Due to World War II, the United States played a major role in developing penicillin’s large scale production, bringing the once limited supply to an international audience.
Today, antibiotics are widely used in our modern medicine. The Center for Disease Control has recognized that antibiotics are overprescribed.
“In 2015 alone, approximately 269 million antibiotic prescriptions were dispensed from outpatient pharmacies in the United States, enough for five out of every six people to receive one antibiotic prescription each year. At least 30 percent of these antibiotic prescriptions were unnecessary.7www.cdc.gov/”
In our clinic, we commonly see people who are regularly prescribed antibiotics. Often they have a history of recurring illness and infection. Unfortunately, after they finish with their antibiotic treatment, they are more susceptible to illness and infection and are prescribed more antibiotics. This also leads to increased resistance so they need stronger and stronger antibiotics. Eventually they may become fully resistant and their options for medical treatment are severely limited. They are caught in a cycle of deteriorating health.
Some of the most common conditions that are prescribed antibiotics are ear pain, sinus infection, cough or respiratory infections, sore throat, colds and flus, urinary tract infections, asthma, allergies, and other miscellaneous infections.
Chinese medicine has a long history of treating these conditions. It uses the body’s own resources as well as diet and environment to allow the conditions to resolve. It uses acupuncture, herbal medicine, and other recommendations such as hydration, rest, appropriate food, and healthful environment.
We regularly assist people in their goals to break the antibiotics cycle for urinary tract, sinus, ear, and lung infections as well as allergies, asthma, and cold and flu symptoms.
By treating these conditions and allowing the body to recover, we build up the body’s resistance to future ailments. After the pathogen resolves, we continue to strengthen the immune system and the body’s capacity for robust health and in doing so, prevent a recurrence of the infection, breaking the cold/infection/inflammatory cycle.

Garth Reynolds, MSTCM, L.Ac.
Licensed Acupuncturist and Clinical Herbalist | Schedule Your Acupuncture Appointment
Martial Arts Instructors with Bagua Internal Arts | Local & Online Classes Weekly
#Acupuncture #AcupunctureWorks #AcupunctureBenefits #NaturalHealth #AcupunctureLongmont #HolisticWellness